- altitude
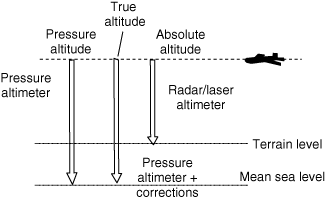
- i. The vertical distance of a level, a point, or an object considered as a point, measured from mean sea level (ICAO). In the case of aircraft in flight, it is normally expressed in flight levels or hundreds of feet. For example, an aircraft flying at 25,000 ft AMSL (above mean sea level) would be said to be flying at flight level 250. A barometric altimeter shows pressure altitude. When it is corrected for instrument errors and necessary compensation is made for variation from standard atmospheric conditions, it is called a true altitude. Absolute altitude is measured by a radio, radar, or laser altimeter. Absolute altitude is the true distance from the surface of the earth at that point. In some definitions, heights, which are the vertical distance of an object from an object, point, or level above ground or other reference plane, are also called altitude, such as in AGL (above ground level) altitude, MSL (mean seal level) altitude, and indicated altitude (that indicated by an altimeter).
 ii. The angular displacement above the horizon; the arc of a vertical circle between the horizon and a point on the celestial sphere measured upward from the horizon from 0° to 90°. Angular displacement below the horizon is called negative altitude, or dip. See also computed altitude and density altitude.
ii. The angular displacement above the horizon; the arc of a vertical circle between the horizon and a point on the celestial sphere measured upward from the horizon from 0° to 90°. Angular displacement below the horizon is called negative altitude, or dip. See also computed altitude and density altitude.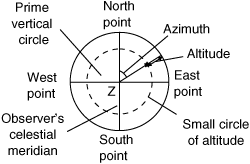 Altitude (celestial).
Altitude (celestial).
Aviation dictionary. 2014.
